Maps of Kelly Lake
Township Map
Kelly Lake is located in McKim, Broder, and Waters townships.
UTM Coordinates:
Easting 494785, Northing 5143348
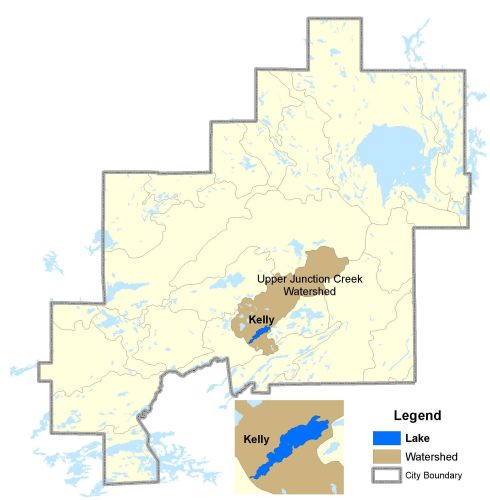
Watershed Map
Kelly Lake is located in the Upper Junction Creek Watershed. Its 207km watershed includes the mining, milling and smelting complex operated by INCO, one of the largest such complexes in the world. The landscape in the Kelly Lake watershed suffered severe erosion after losing its vegetation first to logging and then to sulphur dioxide fumes and fuel-wood cutting when open roasting and smelting of ore began in 1888.
Kelly Lake was also heavily impacted by the discharge of untreated sewage into the lake until 1972 when the Sudbury Sewage Treatment Plant was built.
For more information on the watershed, and on the data obtained for this lake, please click on the following link: Watershed Map
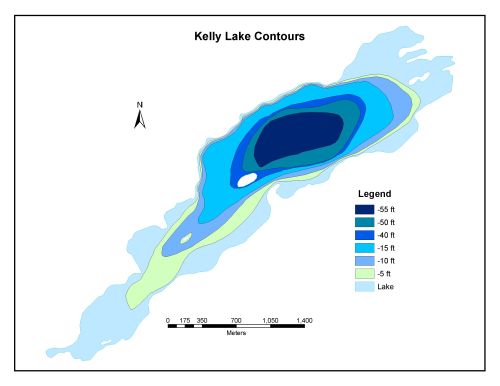
Bathymetric Map
Kelly Lake is 340.8 hectares in size with a shoreline perimeter of 15.5 kilometers. The maximum depth of Kelly Lake is 18 meters (55 feet). Kelly Lake is an elongate, eutrophic lake, approximatively 4.5km long by 1km at its widest point.
Since the 1880's (early settlement in Sudbury) Kelly Lake has been the major sink for contaminants from a mining community due to its location at the foot of Sudbury's watershed. This is seen by the 120cm of metal rich, nutrient rich sediment that has accumulated in the eastern basin of the lake.
Kelly Lake is divided into 2 very different morphological components: a steep sided, 16 to 18m deep eastern basin and a shallow 2 to 4m deep western shelf. The eastern basin functions as a sediment trap, aided by prevailing westerly winds and pronounced stratification at 11m during the summer, followed by four to five months of ice cover in the winter. On the other hand, the western shelf, with a much lower depth relative to area, is susceptible both to periods of sediment resuspension driven by wind mixing and to erosion during periods of high flow, especially during spring runoff. As well as influencing sedimentation, the difference in the two environments has considerable implications for the means by which contaminants in the sediment are transferred to the water column and thereby moved downstream.